Appointments:
Mo. - Th.: 08:00 - 15:00 Uhr
Fr.: 08:00 - 13:00 Uhr
Outpatient Appointments:
Tel.: 0391/67-15529
Fax.: 0391/67-21407
Centralized Patient Management:
0391/67-21401
Interdisciplinary Reflux Consultation
Appointments and Queries
Tuesdays,
11:00 Uhr - 13:00 Uhr
Prof. Dr. med. F. Benedix
PD Dr. med. U. von Arnim
Tel.: 0391/67-15529
Fax: 0391/67-21407
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
Reflux disease is caused by a pathologically increased reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus. This normally occurs only rarely and is prevented by a type of valve between the esophagus and stomach (lower esophageal sphincter). Increased reflux of stomach contents into the esophagus leads to typical symptoms such as heartburn and acid regurgitation. These symptoms are often aggravated in a lying position or by bending over.
In some patients, inflammation of the esophagus occurs, which is visible as erosions during gastroscopy. In a large proportion of patients, however, the mucosa of the esophagus appears completely inconspicuous during endoscopy despite pronounced symptoms.
Few patients with heartburn have changes in the esophagus associated with an increased risk of developing adenocarcinoma (esophageal cancer). In these patients, there is a replacement of the normal mucosa of the esophagus with a special mucosa (Barrett's mucosa). In this situation, a specific endoscopic examination is necessary. Hereby, the risk for cancer development can be assessed more accurately and potential precancerous lesions can be treated.
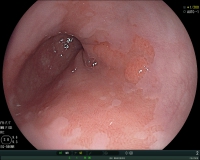
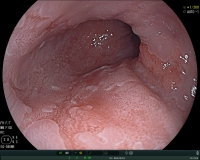
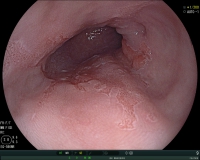
Visualization of a Barrett's mucosa during gastroscopy (view of the lower esophageal portion).
Causes of reflux are manifold:
- Hiatal hernia
- - Overweight
- - weakening of the valve mechanism
- - certain medications
- - alcohol, nicotine
- - increased pressure in the stomach (e.g. emptying disorder)
At Magdeburg University Hospital, we have established an interdisciplinary consultation for patients with reflux disease. This is run by physicians from the Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Infectiology and the Department of General, Visceral and Vascular Surgery. In this joint consultation, the first step is a detailed assessment of your symptoms and your current treatment. If further examinations are necessary, they will be organized by us. After completion of the diagnostics, a therapy recommendation is made on the basis of these findings.
Important examinations
For the treatment of reflux disease and evaluation of different therapy options, it is necessary to objectively examine the reflux disease and function of the esophagus. This is based on a high-resolution endoscopic examination of the stomach and esophagus (gastroscopy). Here, the presence as well as the extent and severity of the inflammation can be precisely assessed. In addition, the size of the frequently existing diaphragmatic hernia can be estimated.
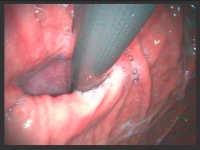
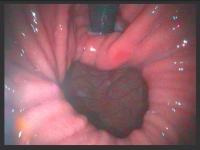
Visualization of a diaphragmatic hernia during gastroscopy. View in inversion. Right: paraesophageal hernia; left: axial hernia.
Further functional examinations performed on an outpatient basis are usually necessary for the exact therapy decision. These are performed in our gastroenterologischen Funktionslabor .
pH metry / combined pH impedance measurement
A thin catheter inserted transnasally is used to measure over 24 hours how frequently stomach contents cross over into the esophagus and cause symptoms there. This examination is performed on an outpatient basis. This means that the probe is placed in the clinic and the measurement takes place over 24 hours as an outpatient in the home environment.
High Resolution Manometry
Manometry (pressure measurement) examines the movements of the esophagus during normal swallowing processes. The imaging of the movement patterns of the esophagus (motility) succeeds in high resolution by special manometry catheters and is performed in patients with dysphagia and before planned operations (e.g. in reflux disease).
This examination is also performed on an outpatient basis and usually takes no longer than 10-20 minutes.
Treatment of Reflux Disease
The initial therapy for reflux disease is always drug therapy, i.e. non-surgical treatment. Surgery should only be considered in case of failure or intolerance of drug therapy. In addition, a change in lifestyle is important (weight reduction; avoidance of nicotine, coffee, alcohol; small meals).
If conservative therapy measures have not led to lasting success, or if permanent drug therapy is not possible, surgery may be helpful. For this purpose, a detailed discussion and extended diagnostics are necessary, since not all patients benefit from surgery.
Surgical Therapy
Laparoscopic fundoplicatio (surgery in "keyhole technique)
During the operation itself, a minimally invasive technique is used to narrow the usually widened diaphragmatic gap (passage of the esophagus) and to place the upper part of the stomach as a sleeve around the lower sphincter of the esophagus.
Minimally invasive implantation of a pacemaker (EndoStim)
As an alternative to fundoplicatio, a pacemaker system can be used. Here, small electrodes are implanted in the area of the weakened sphincter muscle and connected to a control device implanted in the subcutaneous fatty tissue (comparable to a cardiac pacemaker). The stimulation leads to an improvement in the function of the sphincter muscle.
We would like to work out which therapy is most suitable for you together in our consultation. If you are not sure whether you suffer from reflux disease, you can fill out the following questionnaire (http://reflux-test.com/de-es/uniklinikum_magdeburg).
If you would like to contact us, please send us the completed questionnaire online. Alternatively, you can make an appointment for our consultation hours by telephone.
Contact Person:

Prof. Dr. med. Frank Benedix PD Dr. med. Ulrike von Arnim
Klinik für Allgemein-, Viszeral-, Klinik für Gastroenterologie,
Gefäß- und Transplantationschirurgie Hepatologie und Infektiologie
What is needed at presentation:
- referral slip
- Existing examination findings in written form
- CD's if radiological diagnostics are available
- current medication






